Nickel and Cyanide Anomalies Detected Around Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Raise Questions
A recent study using data from the Very Large Telescope (VLT) has uncovered surprising chemical anomalies surrounding the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS, sparking renewed discussions about its possible origins.
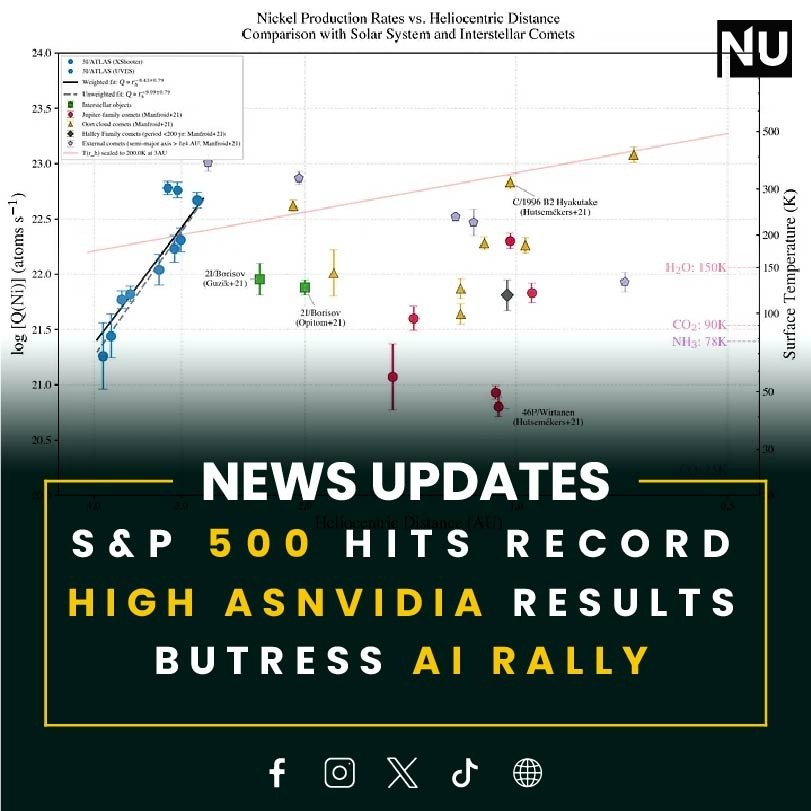
The research revealed the unusual presence of nickel without iron in the gas plume around 3I/ATLAS. Typically, natural comets display both nickel and iron together, as these elements are generally formed side by side in supernova ejecta. Detecting nickel in isolation is unexpected and, intriguingly, resembles methods used in industrial nickel refining.
Alongside this, the data also confirmed significant amounts of cyanide (CN), with a mass-loss rate of about 20 grams per second at 2.85 AU. Even more remarkable is the sharp rise in both nickel and cyanide emissions as the comet approaches the Sun, suggesting processes that differ greatly from those in typical comets.
Earlier observations from SPHEREx and the James Webb Space Telescope already hinted at anomalies, showing that 3I/ATLAS is composed of 95% carbon dioxide and only 5% water, a stark contrast to the water-rich composition of standard comets. The absence of a prominent cometary tail in Hubble Space Telescope images further complicates the picture.
If sunlight is being reflected mainly by the nucleus itself, the object could be far more massive than previously thought — possibly a million times more massive than the interstellar object 2I/Borisov. Some researchers suggest that the trajectory of 3I/ATLAS, which aligns closely with the ecliptic plane of our solar system, may not be random but instead point toward a technological design.
These findings, presented at the “Current Themes in Astrophysics and Particle Physics 2025” conference in Copenhagen, are fueling debates among astrophysicists about whether 3I/ATLAS could represent more than just a natural interstellar visitor.
As investigations continue, 3I/ATLAS stands out as one of the most puzzling objects ever detected beyond our solar system — raising questions about cosmic chemistry, cometary behavior, and perhaps even the possibility of advanced technology.