“96% of World’s Oceans Are Burning: Record 525-Day Marine Heatwaves Trigger Coral Death and Billions in Fishery Losses”
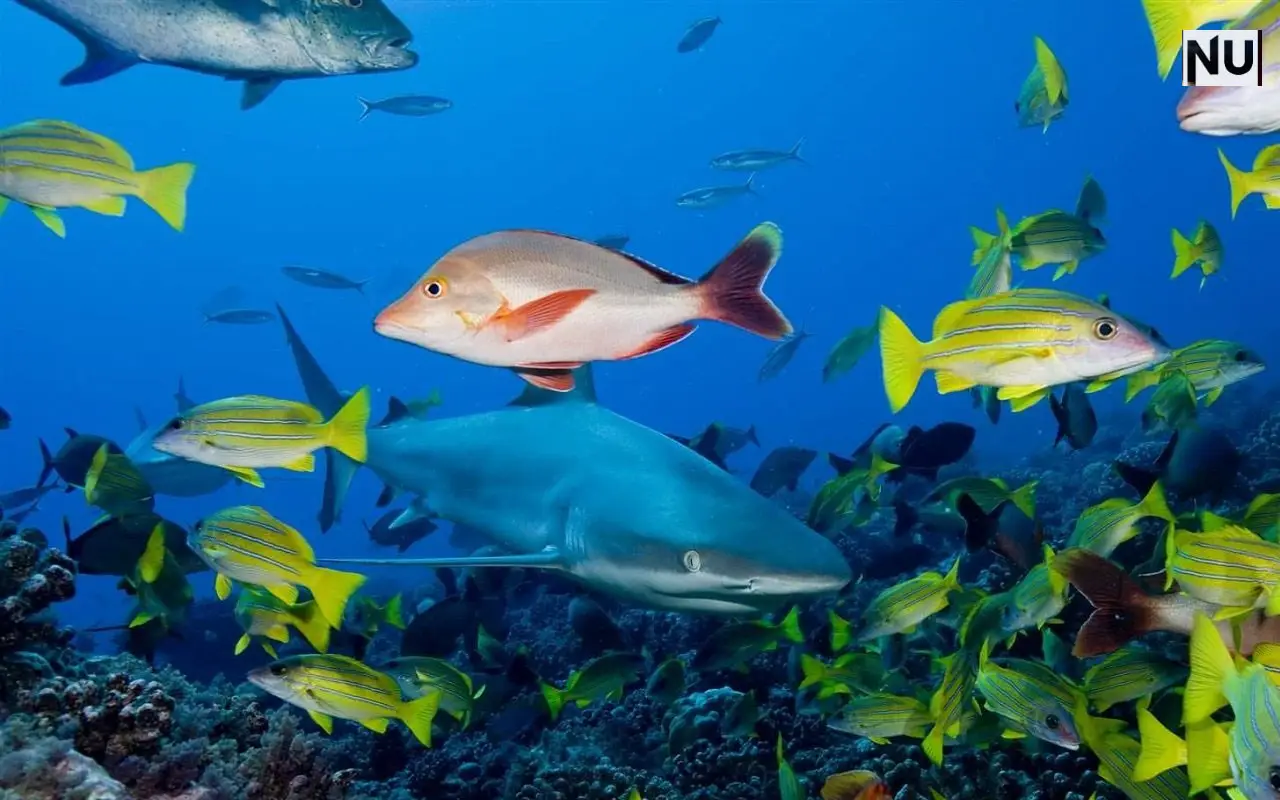
In 2023, the planet witnessed an alarming climate crisis as marine heatwaves 2023 swept across 96% of the world’s oceans. These extreme temperature surges persisted for an astonishing 525 days, making it the longest and most widespread ocean heatwave event in recorded history. Scientists warn this global-scale phenomenon signals a potential tipping point in Earth’s climate system, with devastating impacts on marine ecosystems and human livelihoods.
For more climate updates, visit News Updates.
Understanding Marine Heatwaves and Their Rising Threat
Marine heatwaves are defined as prolonged periods when ocean temperatures rise well above average. While such events have occurred in the past, 2023 marked a dramatic escalation. A study in Science revealed that these heatwaves lasted four times longer than historical averages, spreading across critical regions such as the North Atlantic, Tropical Pacific, and North Pacific.
This sudden temperature rise leads to coral bleaching, reduced oxygen levels, and massive disruptions in marine food chains. Once stable ecosystems are now on the brink of collapse, forcing marine species to abandon their natural habitats.
Record-Breaking Global Spread and Duration
The scale of marine heatwaves 2023 was unprecedented. Almost every ocean basin, from the Southwest Pacific to the Atlantic, registered heat spikes. In some areas, water temperatures surged by up to 2.9°F above normal, intensifying coral bleaching and triggering El Niño patterns.
The North Atlantic was one of the hardest-hit regions, with heat anomalies lasting a staggering 525 days, a record unmatched in history. According to NOAA, such events are likely to intensify as greenhouse gas emissions continue to fuel global warming.
Why Did Marine Heatwaves 2023 Become So Extreme?
Scientists attribute the severity of these heatwaves to both natural climate cycles and human-induced warming. Reduced cloud cover, altered ocean currents, and changes in wind patterns contributed to the oceans absorbing more heat.
However, the primary driver remains global climate change. Rising greenhouse gases have raised baseline sea temperatures, creating conditions where even minor anomalies spiral into extreme heatwaves. Once these feedback loops lock in—such as reduced ocean mixing and surface heat trapping—the result is prolonged ocean warming.
Coral Reefs: The First Victims of Ocean Heating
Among the worst casualties of marine heatwaves are coral reefs, often called the rainforests of the sea. These ecosystems host thousands of marine species, but they are extremely sensitive to temperature spikes.
When exposed to heat stress, corals expel the algae living in their tissues, causing bleaching. If temperatures remain high, corals die, leading to ecosystem collapse. Marine biologists warn that many reefs may never recover if extreme events like marine heatwaves 2023 become the new normal.
Fisheries and Economic Collapse Worth Billions
The global fishing industry, valued at billions of dollars annually, is now facing existential risks. Rising temperatures disrupt fish breeding cycles, feeding patterns, and migration routes.
Communities reliant on fishing in Asia, Africa, and the Americas are already experiencing shrinking catches. Studies suggest that the economic cost of marine heatwaves 2023 could exceed billions in lost fishery revenue, alongside food insecurity for millions who depend on seafood as a staple.
The Bigger Climate Picture: Tipping Points Approaching
The severity of marine heatwaves 2023 highlights a critical warning: Earth’s climate is edging closer to irreversible tipping points. Rising sea temperatures accelerate polar ice melt, fuel stronger hurricanes, and push sea levels higher.
If oceans lose their ability to act as climate buffers, global warming will escalate even faster. This chain reaction could destabilize weather systems worldwide, making adaptation increasingly difficult for both ecosystems and human societies.
The Urgent Call for Action
Experts emphasize the need for immediate international action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and strengthen global climate agreements. Strategies include:
-
Expanding marine protected areas to safeguard ecosystems.
-
Investing in sustainable fisheries management.
-
Accelerating the shift to renewable energy to cut carbon emissions.
-
Enhancing scientific monitoring of marine heatwave patterns.
The marine heatwaves 2023 crisis is more than an environmental issue—it is a global survival challenge that links climate, biodiversity, and human security.
-
Internal Link: News Updates
-
External Link: NOAA